




Bromelain
Bromelain is a group of natural enzymes extracted from pineapple stem by microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and vacuum freeze-drying. Its main component is a sulfhydryl-containing protease with a molecular weight of 33,000.
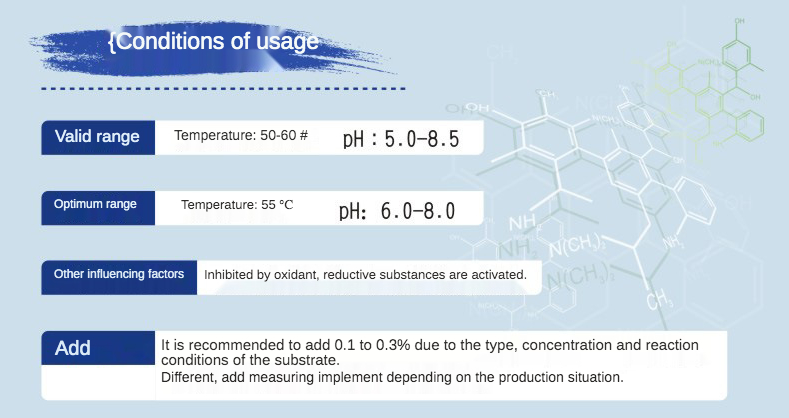
The active center of bromelain contains cysteine, which is a sulfhydryl endoprotease. It also contains peroxidase, acid phosphatase, several protein inhibitors, and organic active calcium. Bromelain can hydrolyze all kinds of proteins and carry out biochemical reactions, making it suitable for use in food, medicine, biology, and other industries.
The product is soluble in water, and the water solution is a colorless or rice soup-colored liquid.
Bromelain is a natural, non-toxic, and side-effect-free protein. As a sulfhydryl hydrolysis protease, it can be used to hydrolyze protein molecules, producing polypeptides or amino acids, and creating protein hydrolysates with a unique flavor.




